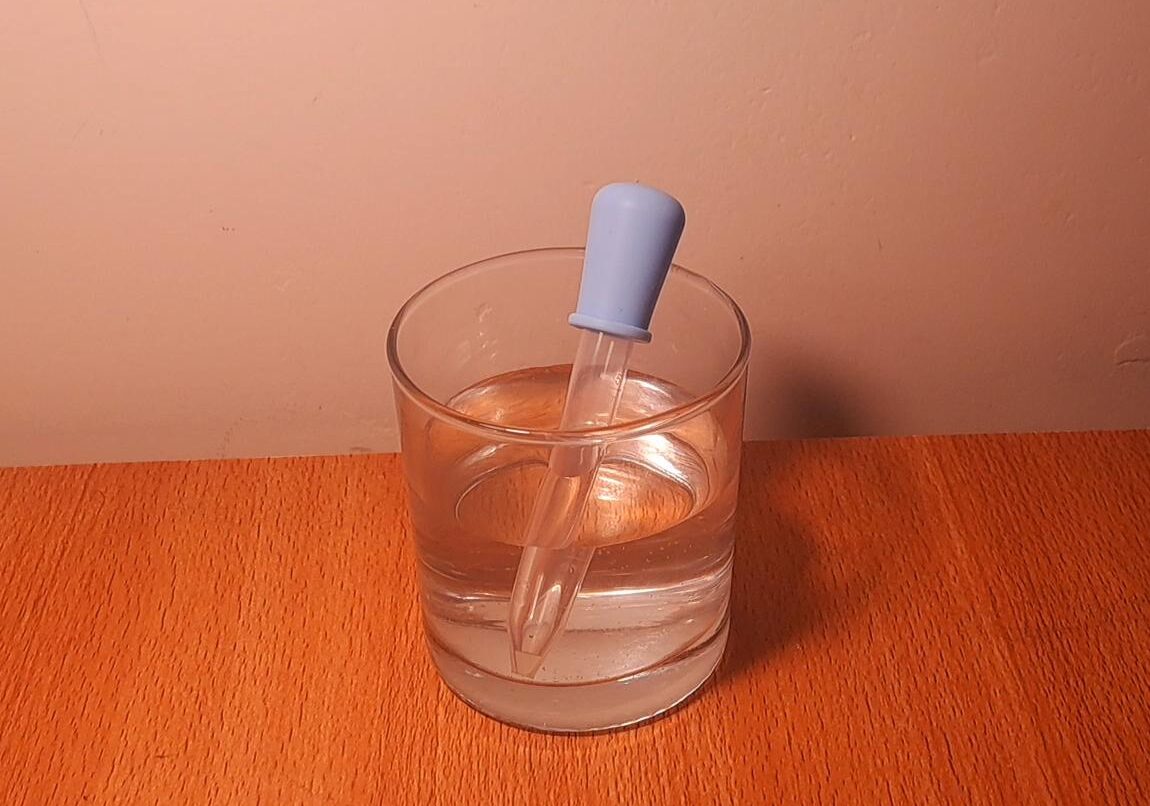
A water dropper is device that works by utilizing the atmospheric principles of atmospheric pressure of air and suction. It is also known as pipette.
It has many practical applications ranging from providing controlled dose of medicine to infant to putting the droplets in eye. You will find its use in chemistry lab in order to add the controlled concentration of a fluid in a solution.
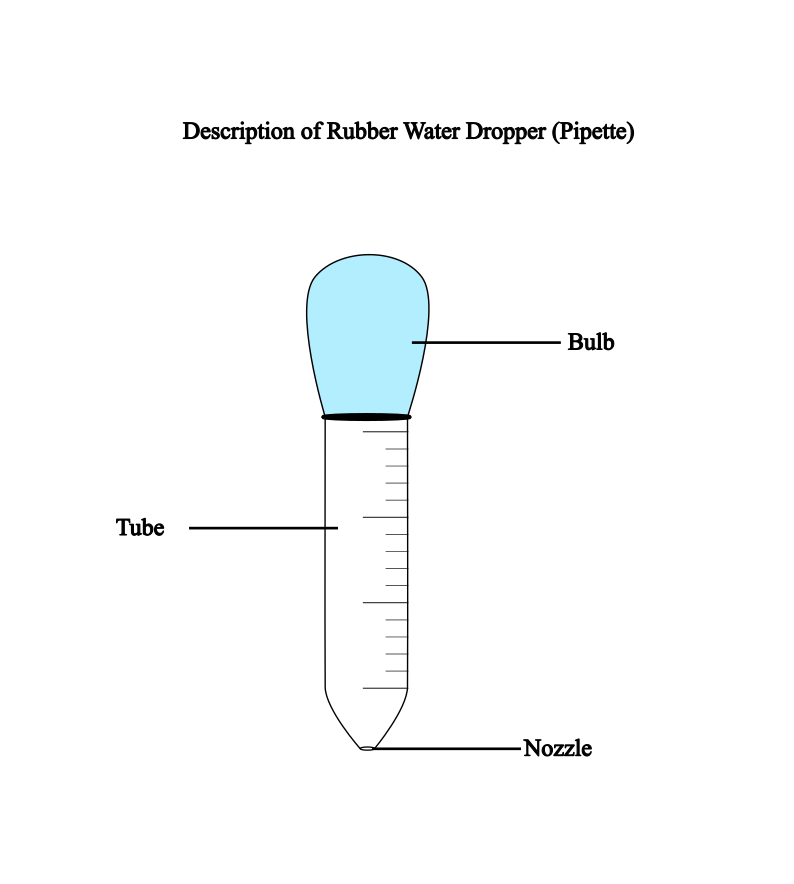
It has two main components namely a bulb and a tube with a small nozzle at the bottom. It comes in different shapes and sizes but the basic principle is the same.
How it works?
When you insert the dropper in any fluid say in water and press its bulb; the air inside the dropper is released in the form of bubbles from the nozzle immersed in water.
When the pressure on the bulb is released, this causes the low air pressure (or vacuum) inside the dropper as compare to the outside air pressure. The vacuum created inside the bulb cause the liquid to be sucked in the tube.
If you now remove the dropper from the water reservoir, you will observe that water inside the dropper tube won’t drain from the nozzle of the dropper. This is because the air pressure outside the dropper is higher as compare to air pressure inside. This outside air pressure exert a force the water and hence act a seal which prevent water to leak from the nozzle.
In order to release the water inside the dropper, squeeze the bulb again and the water will start flowing from the dropper nozzle.
Hence by controlling the amount of pressure applied to bulb the user can control the amount of fluid that is sucked in or released from the dropper.

