What is an Electrical Circuit
An electrical circuit is closed path through which electric current flows. We know that all kinds of electric equipment operate when electric current flows through them and that happens when there is an electric circuit through which the current flows in a loop.
Components of Electrical Circuit
An electric circuit typically consists of following components:
1. Power source
It is source that provides electrical energy and generates electric current that flows through the circuit. For more details on electrical energy is generated, please refer to Learn how electricity is generated with this DIY hand crank electric generator? Batteries and electric generator are some examples of the power sources.
2. Load
Load is anything which consumes electricity. Load typically takes electricity and converts it into other forms of energy. Electric bulb, electric heater, electric fan are all example of load.
Batteries can act both as power source and as load. When batteries are being charged they act as load because the take electricity store it as chemical energy.
When batteries are being discharged, they act as power source because chemical energy stored in batteries are converted into electricity which can then be used to operate any other load in the circuit.
3. Conductors
Conductors carry electricity from the power source to the load.
4. Switches
Switches allow the circuit to be in open (turn on) or close (turn off) position.
Complex circuits may consist of many other components such as resistors, capacitors and inductors, which are not covered here. Electric circuit can be categorized in many ways however two most common types are as follows:
Types of Electrical Circuit w.r.t Current
There are two types of electric circuit depending upon what kind of electric current is passed through the circuit:
- Direct Current (DC) circuit
- Alternating Current (AC) circuit
Direct Current (DC) circuit
It is type of electrical circuit in which the current flows in single direction. In DC circuit, a steady current or voltage is maintained over time.

Commons source of DC power includes batteries, solar panels and DC power supplies etc.
Alternating Current (AC) circuit
In Alternating Current (AC) circuit, the current changes is direction and magnitude periodically over time. AC circuit is the most common type of circuit used in our homes, industry and businesses worldwide.
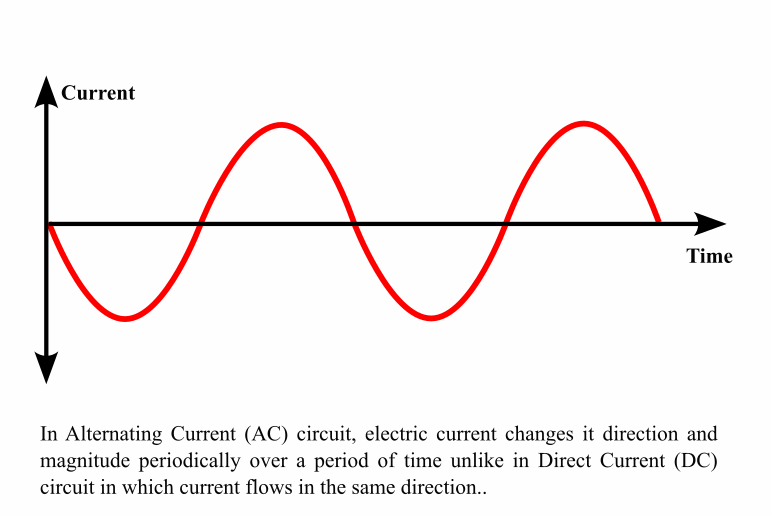
Commons source of AC power are AC generators which generates electricity on larger scale.
Types of Electrical Circuits w.r.t Connection
With respect to connections, an electrical circuit can be categorized into following types:
- Series Circuit
- Parallel Circuit
Series Circuit
Series electrical circuit is a type of circuit in which load sources are connected in end-to-end path.
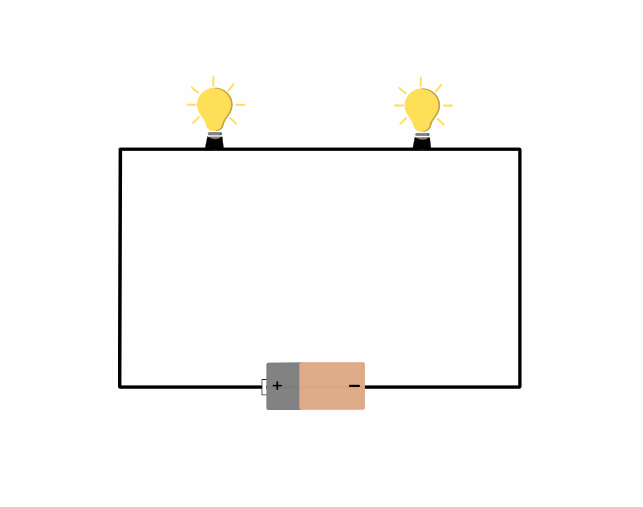
Example of series circuit
In series circuit, current flows through each component one after the other through the same path.
Key Characteristics of Series Circuit
- The current flows through all components are same because there is only one path for the current to take.
- Voltage across the circuit is the sum of the voltage across each component.
- If one component in the circuit fails (e.g., a bulb burns out), the entire circuit is interrupted, and current will not flow.
Parallel Circuit
In a simple parallel circuit, the load sources are connected across the same two points and are independently connected to the power source.
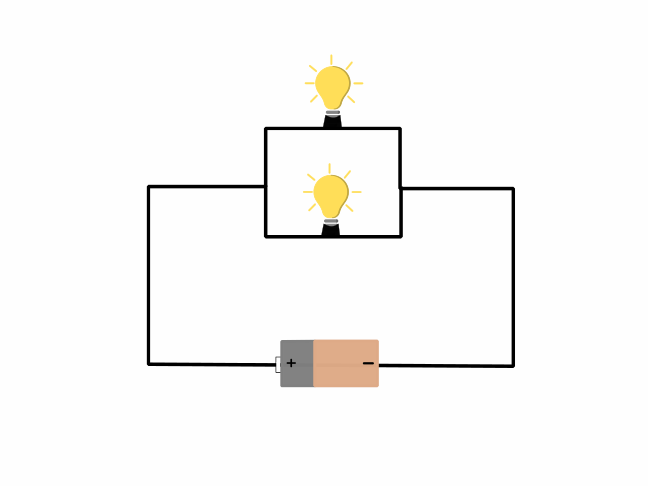
Example of Parallel Circuit
Key Characteristics of Parallel Circuit
- The total current in the circuit is the sum of the currents flowing through each parallel branch. This is because the current splits and flows through each branch according to its resistance or impedance.
- The voltage across each component in a parallel circuit is the same because they share the same connection points.
- If one component fails or disconnected, the other branches remain operational because they are independently connected to the voltage source.
Note: A complex electric circuit can be a combination of both series and parallel circuit.
