In our daily life, we hear a lot of different sounds; sound of other people, sound of car, sound of water flowing, sound of different animals etc. Have you ever wonder how sound is generated and how do we hear the sound waves?
How Sound Waves are formed?
Let’s take a simple example. Throw a stone in a water lake. As soon as the stone hit the water surface it will generate a splashing sound wave. What happens is when stone hits the water surface, it cause the surface to vibrate. That vibration is carried by the surrounding air molecules. Note that air molecules are in constant random motion. So when vibrating water surface hit the surrounding air molecules, those molecules travel faster and consequently bump into the slower molecules thereby transferring their momentum to these slow molecules which then move faster. These molecules then bump into next slower molecules and again transfer their momentum. This process continues till the sound waves pass through our ears and hit our ear drums. That’s how we hear a sound of splashing water.
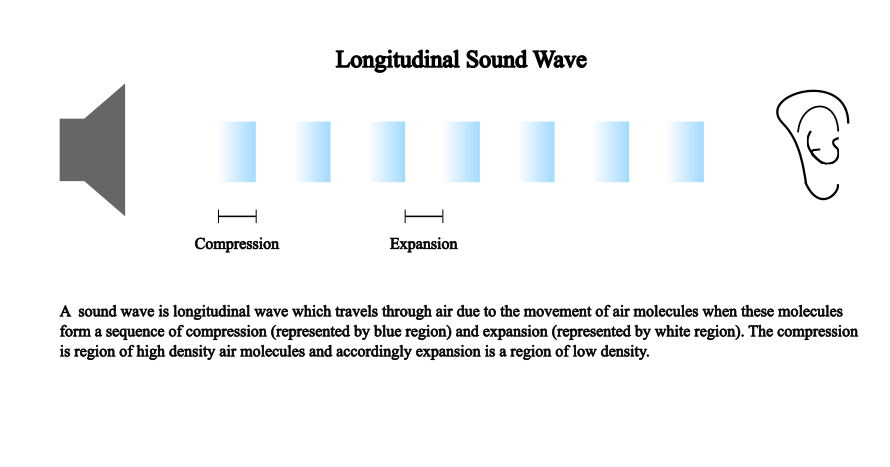
Key features of Sound Wave:
- Sound wave is a longitudinal wave which means that particles of the medium vibration in the direction in which the wave travel.
- The region where fast moving air molecules hit the slow-moving air molecules are the region where the density of air becomes higher. These high density region are called the compression region of the wave.
- Sound wave is an energy wave which means that it carries energy and transmit it from one place to another.
- Air is not the only medium through which sound wave travels. Sound waves can travel through almost any medium such metals, woods, liquids and gases.
- The speed of sound waves may vary and it depends upon the medium through which it travels.
To better understand how sound waves , try our Make your own Sound Wave widget. It lets you hear the wave in realtime by selecting the type of wave and adjust frequency and amplitude.


1 thought on “What are sound waves and how are they formed?”